
When we hear of cholesterol, it is not always in a positive sense. Given its association with heart diseases, over the years, it has earned itself a bad name. But what most people are unaware of is that cholesterol is indeed a useful substance that the body uses to build cells, make hormones like oestrogen, testosterone and adrenal hormones, and boost metabolism. Additionally, cholesterol is divided into two different types namely Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and interestingly, the latter is actually “good” for the heart.
Table of Content:-
Also Read: THIS Cholesterol Symptom Could Strike At Night: Other Warning Signs To Note
What Is High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol?
According to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), cholesterol moves through the blood on proteins called 'lipoprotein'. These are classified into types LDL and HDL cholesterol.
While LDL or "bad" cholesterol accounts for most of your body’s cholesterol, HDL cholesterol absorbs excess cholesterol in the blood and carries it back to the liver, where it is excreted from the body, explains the CDC.
Therefore, high levels of LDL cholesterol contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries, raising the risk of heart disease, whereas high levels of HDL cholesterol absorbs the excess fatty substance and lowers the risk for heart disease and stroke.
HDL And Heart Health
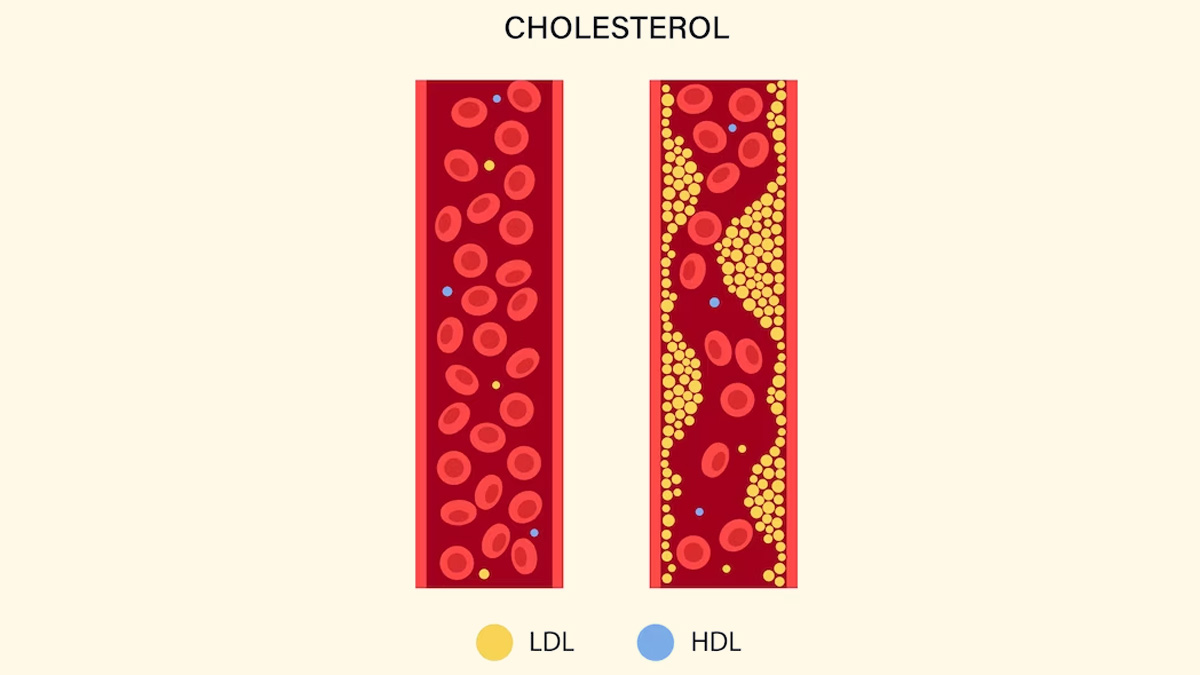
HDL cholesterol supports heart health by assisting in removing excess cholesterol from the arteries, which in turn reduces the risk of plaque buildup and blockages.
Moreover, it contains anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that protect blood vessels and reduce the risk of inflammation-related damage. Therefore, it is important to note that unlike LDL cholesterol, higher HDL levels are actually good for the heart.
Hence, an HDL level at or over 60 milligrams/deciliter (mg/dL) in men and women are said to be the desirable amount of cholesterol in the body, whereas a cholesterol level less than 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women is considered risky, according to Mayo Clinic.
Also Read: Are You Taking Statins For Cholesterol Management? Here Are Mistakes You Should Avoid
How To Boost HDL Cholesterol Levels

Here are some effective ways to boost and increase your HDL levels:
Regular physical activity, which includes aerobic exercises like brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling for at least 150 minutes per week
- Consuming foods rich in unsaturated fats, such as olive oil, avocados, and fatty fish like salmon and mackerel
- Increasing the intake of soluble fibre, which can be found in oats, beans, and fruits
- Adding sources of omega-3 fatty acids, like fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, into your diet
- Losing excess weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Reducing refined carbohydrate intake and opting for complex carbohydrates
- Alcohol consumption in moderation; best to cut it off
- Quitting smoking as it lower the HDL levels in the body
- If you're on cholesterol-lowering medications, it is best to consult with your doctor before stopping it
Bottomline
HDL cholesterol is extremely beneficial for your heart, especially because it helps in eliminating excess “bad” cholesterol from the body that eventually goes on to increase your risk for heart disease and stroke. It is crucial that you make healthy lifestyle choices, eat foods low in saturated fat, and indulge high-fibre foods and healthy fats. Furthermore, it is a good practice to get your cholesterol levels checked regularly.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version