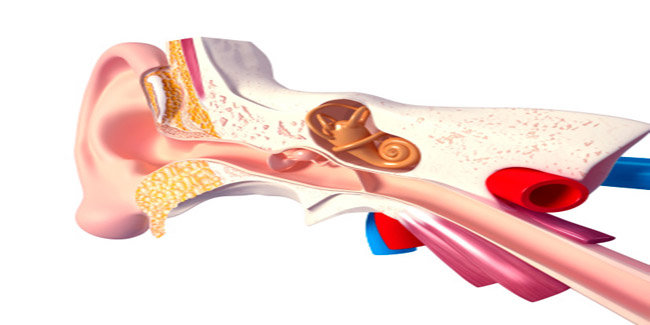
The Eustachian tube is a canal that connects the middle ear cavity with the nasopharynx. It balances the air pressure in the middle ear system with the atmospheric pressure outside the body and clears mucus from middle ear. The tube is usually closed and opens only during activities such as chewing, yawning, and swallowing. These activities can be done deliberately to open the tube whenever there is a sudden change in the air pressure outside the ear.
Table of Content:-

When the tube doesn't open leading to imbalance of air pressure, it usually causes symptoms of dizziness, discomfort, or ringing in the ear. Abnormal Eustachian tube functions may lead to pathological changes in the middle ear which may even cause hearing loss and other complications.
Functions
The tube is important for the health of the ear and an impaired Eustachian tube may cause complications in the air along with discomfort and dizziness. The opening and closing of the Eustachian tube performs three crucial functions. 
Pressure regulation
The normal eustachian tube opens repeatedly during chewing, yawning and swallowing to actively maintain normal atmospheric pressure. When the tube opens up it contracts the tensor veli palatini muscle. Impaired tensor veli palatini muscle function may also lead to eustachian tube dysfunction. The tube is more effective in regulating the pressure inside the air and outside it, among adults as compared to children. In children the tube is less efficient in regulating the pressure. The eustachian tube opens frequently to maintain the middle ear pressure between +50 mm and -50 mm H2 O.
Protection
The Eustachian tube also protects the ear from sudden loud sound. As the tube is usually at rest in a closed state, it dampens when there is a sudden loud sound before they can harm the ear. The Eustachian tube also regularly clears the mucus from the middle ear. When the tube opens, it allows the mucus from the middle ear to drain into the nasopharynx. However, in several cases the closed tube prevents secretions from other parts to move into the middle ear, thus preventing complications. The Eustachian tube plays a crucial role in protecting the ear. Air pressure changes during activities such as swimming or flying in an aircraft may damage the ear, however an effective Eustachian tube may protect the ear from such harm.
Clearance or Drainage
The Eustachian tube also performs an important function of clearing mucus from the middle ear as well allowing drainage of secretions and foreign substances from the middle ear. The function is collectively performed by the mucociliary system of the eustachian tube, the middle-ear mucosa, muscular clearance of the eustachian tube and the surface tension within the tube lumen.
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version