In our fast-paced world, convenience often takes precedence over nutrition. One ubiquitous ingredient that sneaks its way into our diet is salt. While it's essential for various bodily functions, excessive salt intake has been linked to several health issues, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and kidney problems. Now, recent studies suggest that consuming too much salt may also contribute to eczema, a chronic inflammatory skin condition.
Table of Content:-
The Link Between Salt and Eczema
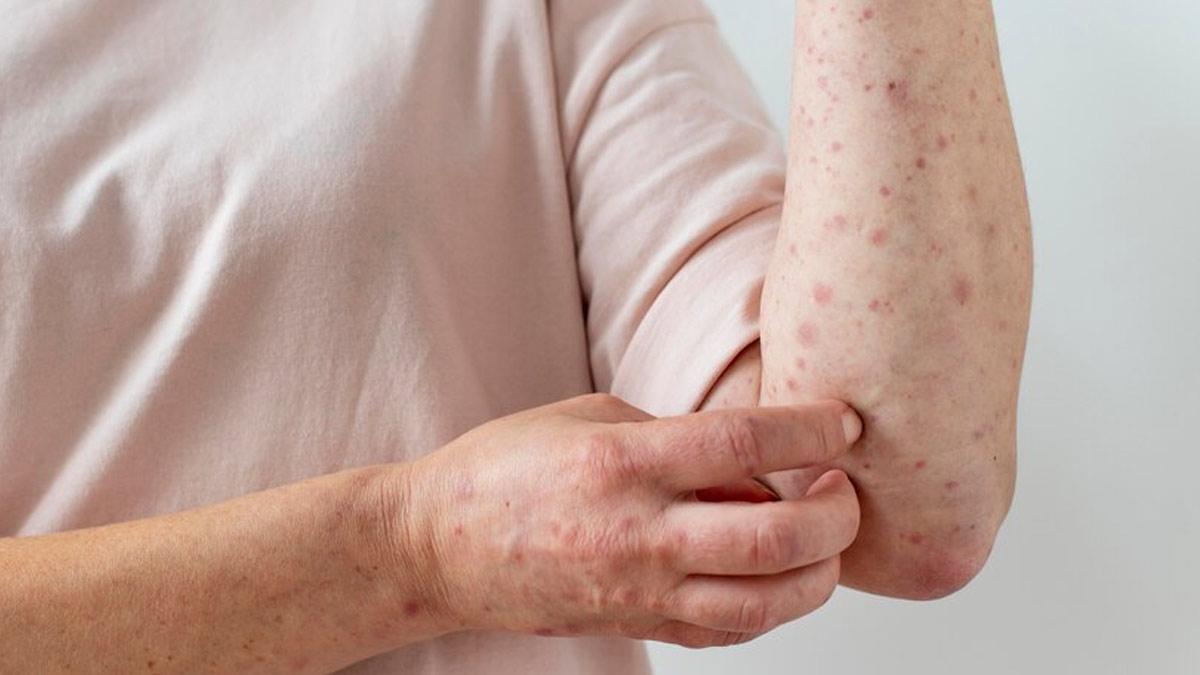
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a condition characterized by red, itchy, and inflamed skin. It affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact the quality of life. The exact cause of eczema remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.

A groundbreaking study published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology has shed light on a new environmental factor—excessive salt consumption. Researchers found that high salt intake could exacerbate the symptoms of eczema and potentially increase its prevalence. The study conducted on mice demonstrated that a diet high in salt led to an increase in immune cells called Th2 cells, which are known to play a crucial role in the development of eczema.
Also read: Dealing With Eczema Scars? Expert Lists Its Causes, Treatment, And Prevention Measures
How Salt Affects the Skin
The skin is the body's largest organ and serves as the first line of defense against external irritants and pathogens. Maintaining the skin's integrity is essential for overall health. When the skin barrier is compromised, as in the case of eczema, it becomes more susceptible to inflammation and infection.
The study revealed that high salt levels can alter the skin's immune response. Salt seems to promote the production of cytokines, proteins that signal the immune system to initiate an inflammatory response. In individuals predisposed to eczema, this heightened immune response can trigger or worsen the condition.
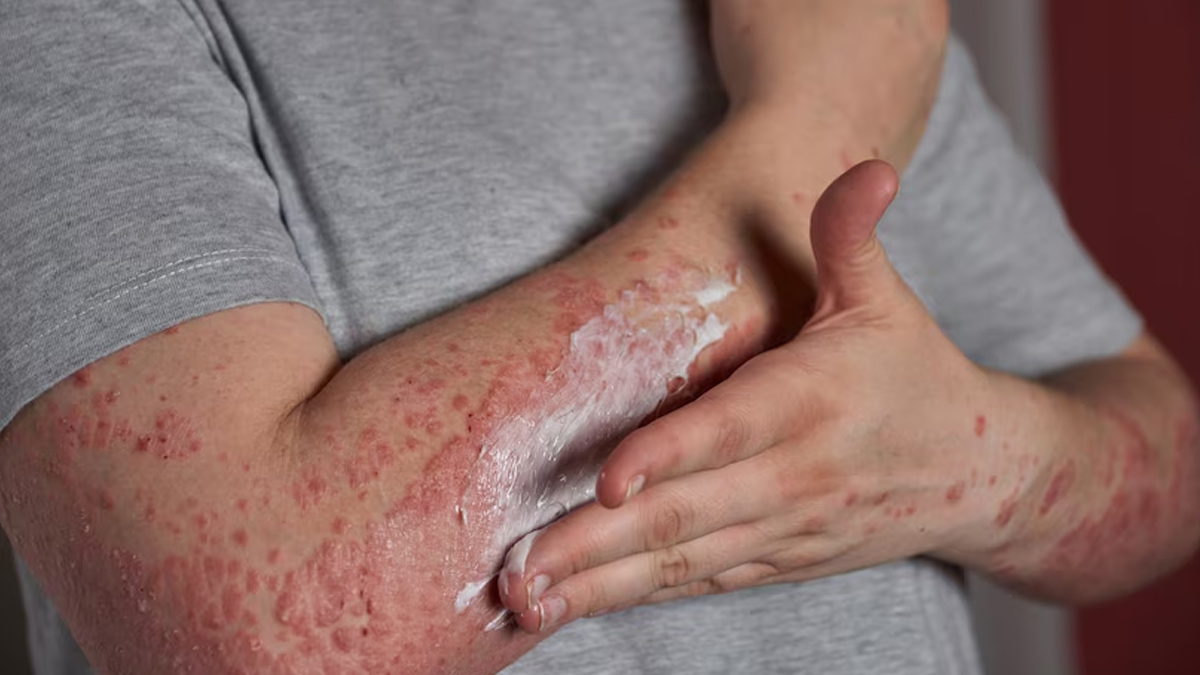
Furthermore, the researchers noted that salt could directly affect skin cells. High salt concentrations were found to impair the function of keratinocytes, the predominant cell type in the epidermis. These cells are vital for maintaining the skin barrier and repairing damaged skin. Impaired keratinocyte function can lead to increased skin dryness, irritation, and inflammation, all hallmark symptoms of eczema.
Implications for Diet and Health
This study's findings highlight the importance of dietary choices in managing and potentially preventing eczema. While it's already known that certain foods can trigger eczema flare-ups in some individuals, this research suggests that reducing salt intake could be a beneficial strategy for those suffering from this condition.
Also read: Eczema Flare-Up In Monsoon: Here's How You Can Prevent It At Home
Practical Tips for Reducing Salt Intake

Reducing salt in your diet doesn't mean sacrificing flavor or enjoyment of food. Here are some practical tips to help you manage your salt intake effectively:
Read Labels: Processed and packaged foods often contain high levels of salt. Check nutrition labels and choose low-sodium options when possible.
Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the amount of salt in your food. Use herbs, spices, and other seasonings to enhance flavor without relying on salt.
Limit Processed Foods: Foods like canned soups, frozen meals, and snacks are typically high in salt. Opt for fresh, whole foods instead.
Be Mindful of Sauces and Condiments: Many sauces, dressings, and condiments are high in salt. Use them sparingly or look for low-sodium alternatives.
Rinse Canned Foods: If you use canned vegetables or beans, rinse them under water to remove some of the salt content.
Conclusion
While salt is an essential nutrient, moderation is key to maintaining good health. The recent study linking high salt intake to eczema underscores the broader impacts of diet on skin health. For those struggling with eczema, adopting a low-sodium diet could be a simple yet effective strategy to manage symptoms and improve overall skin condition. As research continues to unravel the complexities of eczema, one thing is clear: what we eat profoundly influences not just our internal health but also the health of our skin. So, the next time you reach for the salt shaker, remember that a little less salt might lead to a lot more comfort and healthier skin.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
