Cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and atrial fibrillation (AFib), are among the leading causes of death worldwide. While lifestyle factors like diet and exercise play a critical role in maintaining heart health, new research suggests that an often-overlooked habit—flossing—could also be a key factor in reducing cardiovascular risk.
Table of Content:-
A recent study presented at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2025 highlights how regular flossing is linked to a lower risk of stroke and AFib. This research provides further evidence of the strong connection between oral health and cardiovascular well-being.

The Link Between Flossing and Cardiovascular Health
The study analysed data from over 6,000 participants in the ongoing Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, which began in 1987. Researchers focused on the role of flossing in cardiovascular outcomes, independent of other oral hygiene practices like brushing or dental check-ups. Key findings from the study include:
- A 22% lower risk of ischemic stroke among those who flossed regularly.
- A 44% reduced risk of cardioembolic stroke, which occurs when a blood clot travels from the heart to the brain.
- A 12% lower risk of atrial fibrillation (AFib), the most common form of irregular heartbeat and a leading cause of stroke.
These findings suggest that maintaining good oral hygiene, particularly through regular flossing, may help prevent serious cardiovascular events.
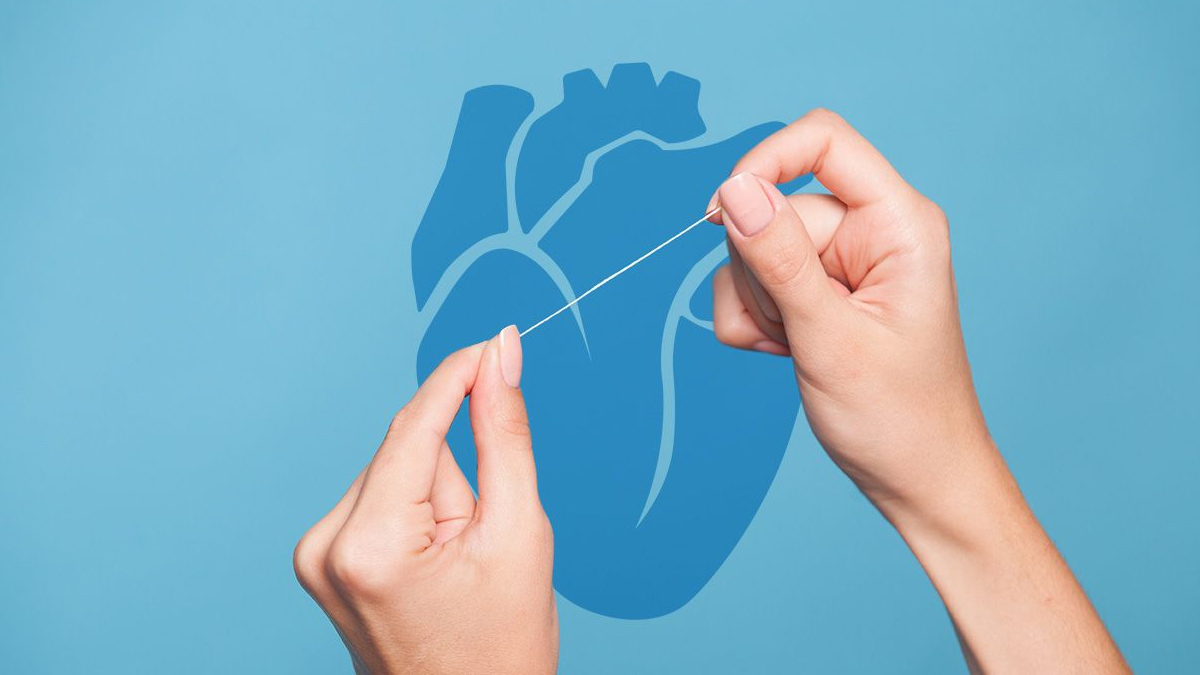
How Oral Health Affects the Heart
The mechanism linking flossing to heart health is not entirely clear, but inflammation appears to play a significant role. Poor oral hygiene can lead to periodontitis, a gum disease that triggers chronic inflammation. This inflammation can then contribute to artery hardening and increase the risk of stroke and heart disease.
Also Read: Humans Of Bombay CEO Karishma Mehta Gets Her Eggs Frozen At 32; Risks Associated With Egg Freezing
Additionally, research has identified harmful bacteria in the mouth that can migrate to the bloodstream and negatively impact cardiovascular health. One such bacterium, Streptococcus anginosus, has been found in higher levels in stroke survivors, particularly in their gut microbiota.
By reducing oral infections and inflammation, flossing may help maintain a healthier cardiovascular system, potentially lowering the risk of stroke and other heart-related conditions.

The Role of Inflammation in Heart Disease
Inflammation has long been recognised as a major contributor to heart disease. Studies suggest that people with chronic inflammatory conditions, including gum disease, are at a higher risk of developing AFib and other cardiovascular issues.
According to Dr Souvik Sen, one of the lead researchers in the study, “Flossing may not only improve oral health but also help in preventing systemic inflammation, which plays a crucial role in heart disease and stroke.”
Also Read: Ebola Outbreak In Uganda: Health Officials Set To Launch Urgent Vaccine Trial
Dr Rod Passman, a cardiologist at Northwestern University, added that while the study highlights a potential link between flossing and heart health, further research is needed to understand the exact mechanisms. He also emphasised that people who floss regularly may engage in other heart-healthy behaviors, which could influence the study's findings.
Simple Steps to Reduce Cardiovascular Risk
While flossing is emerging as a potential tool for heart health, it should be combined with other well-established heart-healthy habits. The American Heart Association (AHA) recommends the following lifestyle changes to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease:
- Eat a nutritious diet – Prioritise whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins while avoiding processed foods and excess sugar.
- Stay physically active – Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Quit smoking – Tobacco use significantly increases heart disease risk.
- Get enough sleep – Poor sleep patterns can contribute to high blood pressure and other cardiovascular issues.
- Maintain a healthy weight – Obesity is a major risk factor for heart disease.
- Monitor cholesterol levels – High cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Manage blood sugar – Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Control blood pressure – Hypertension is a leading cause of heart attacks and strokes.
Bottomline
Cardiovascular disease remains a leading cause of mortality, but new research suggests that simple habits like flossing could play a role in prevention. By maintaining good oral hygiene, individuals may not only protect their teeth and gums but also reduce their risk of stroke, AFib, and other heart conditions.
While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship between oral health and cardiovascular disease, flossing is an easy and inexpensive habit that could have significant health benefits. Coupled with other heart-healthy lifestyle choices, prioritising oral hygiene could be a crucial step toward overall well-being.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version
