
Menopause is a female reproductive milestone that begins in most women between the ages of 45 and 55. It marks the end of the menstrual cycle, and women can no longer conceive, at least not naturally. On the contrary, hypothyroidism is a type of thyroid disease that occurs when the thyroid gland doesn't make enough thyroid hormones to meet the body's needs. The key difference between the two is that menopause isn’t a disease but a normal part of a woman’s life, whereas hypothyroidism is a health condition.
Table of Content:-
Unfortunately, both menopause and hypothyroidism can strike at the same time and sometimes cause overlapping symptoms, leading to confusion and delay in treatments. To help understand the differences and whether one condition may influence the risk of the other, the OnlyMyHealth team spoke to Dr Deepika Alva, Consultant Obstetrician and Gynaecologist, Motherhood Hospitals, HRBR Layout, Bengaluru.
Also Read: How To Manage Freckles During Menopause? Expert Shares Causes and Tips
What Is Menopause?

Menopause is a natural process in the female reproductive system that marks the permanent end of menstrual cycles. It occurs due to a natural decline in the production of female hormones, specifically oestrogen and progesterone, by the ovaries.
While menopause is a natural part of ageing, it can also be triggered by surgical procedures like oophorectomy (removal of ovaries) or certain medical treatments.
Common symptoms of menopause are hot flashes, night sweats, irregular periods, vaginal dryness, sleep disturbances, mood changes, and difficulty concentrating or memory problems.
What Is Hypothyroidism?
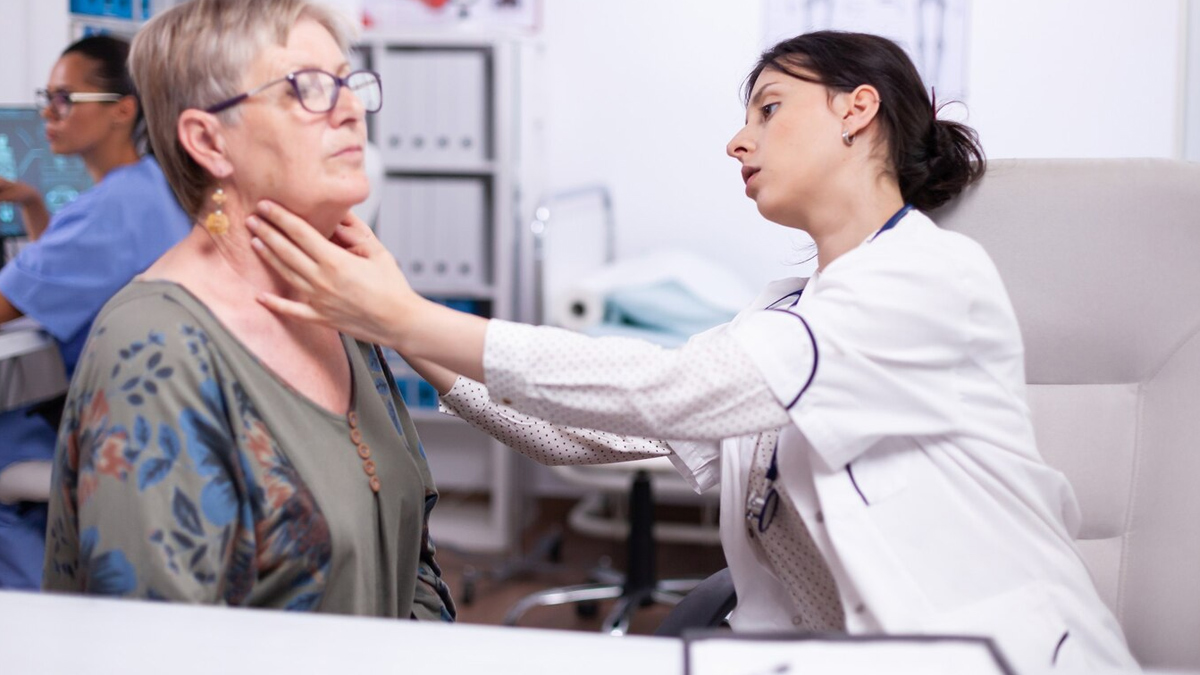
Hypothyroidism, also known as an underactive thyroid, refers to a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. According to StatPearls Publishing, thyroid hormones play a key role in controlling metabolism, growth, and several other body functions.
The thyroid mainly produces two hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones, along with thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) from the hypothalamus and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the pituitary gland, help maintain the body’s balance and hormone levels.
When the thyroid gland is underactive, it leads to hypothyroidism, which can cause symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, constipation, and slow heart rate. On the other hand, an overactive thyroid causes hyperthyroidism, which may result in weight loss, heat intolerance, diarrhoea, muscle weakness, and fine tremors.
How To Tell Menopause Symptoms Apart From Hypothyroidism Symptoms?
According to Dr Alva, hypothyroidism and menopause can be easily confused with each other since both lead to symptoms like fatigue, weight gain, mood swings, dry skin, and irregular menstruation.
However, there are certain distinguishing factors to note.
“If cold intolerance, night sweats, and vaginal dryness are accompanied by fatigue and mood swings, it’s likely menopause,” Dr Alva explained. She added that persistent hair loss along with cold intolerance may be a sign of hypothyroidism.
Monitoring your body's rhythms over the course of several weeks rather than a short few days can provide useful information.
Can Menopause Affect Thyroid Health?
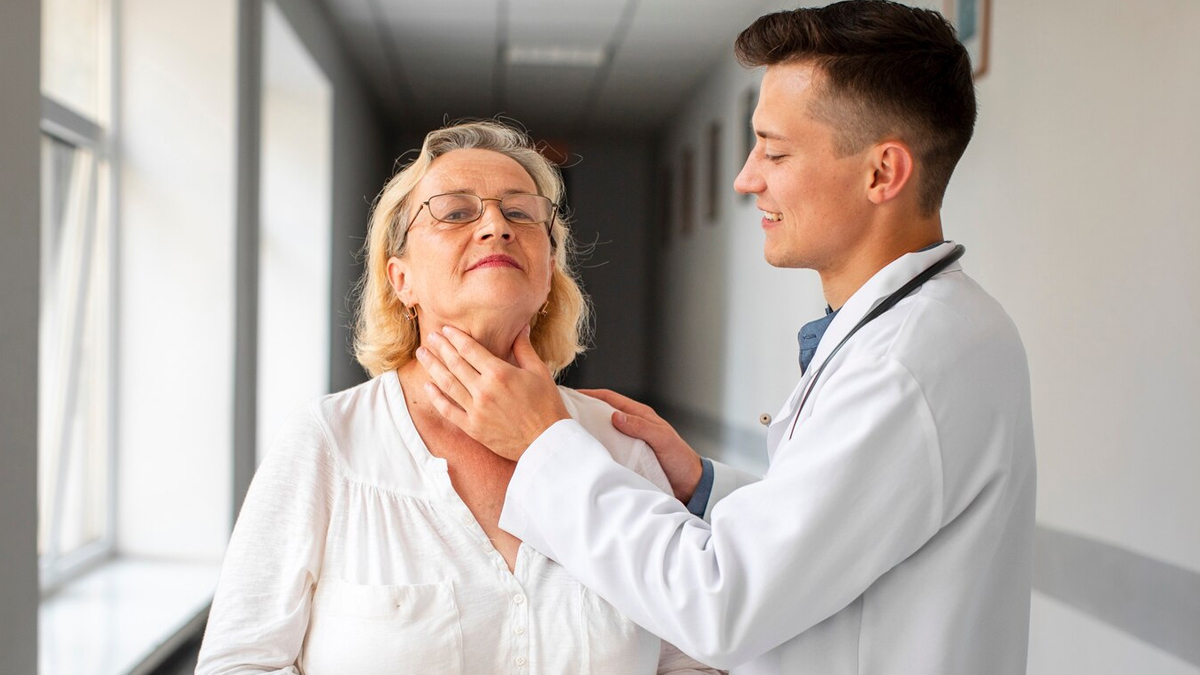
A 2017review published in the Menopause Review found that thyroid issues like hypothyroidism, nodules, and cancer are more common in women over 50. These conditions are harder to spot because their symptoms often look like normal signs of ageing or menopause.
Dr Alva added that menopausal changes can uncover or induce another underlying thyroid disease, particularly with a positive family history or previous thyroid disease. “One can treat menopause and not screen for thyroid issues and vice versa, leading to unexplained symptoms.”
Additionally, untreated thyroid problems can raise the risk of heart disease, weak bones, memory loss, and depression. Treatment needs to be handled carefully, especially in older women, as too much thyroid medication can harm the heart and bones.
Also Read: The Hidden Link Between Gut Health And Hormones: What Every Woman Needs To Know
How To Manage Both Menopause And Hypothyroidism
The key is to get tested and detect thyroid disorders in time. Measuring TSH, T3 and T4 alongside FSH and oestradiol may hypothesise menopause and/or hypothyroidism, said Dr Alva. “Always have the results interpreted by specialists in relation to your symptoms.”
Adding further, the doctor shared that hypothyroidism and menopause can be effectively managed with thyroid hormone replacement, menopause-focused care such as Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) when appropriate, and a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management. What truly makes a difference is personalised care guided by specialists who can tailor treatment to each woman’s unique needs.
Conclusion
Dealing with menopause and hypothyroidism at the same time can feel overwhelming, especially when you don't know what is affecting you more. But you're not alone, and the good news is, with the right tests, support, and a little patience, both can be managed. Understanding what your body is going through and having a doctor who listens and provides appropriate treatment can make a big difference. With the right care and lifestyle changes, it’s absolutely possible to feel like yourself again.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version