
Mumps, a contagious viral infection, primarily affects the salivary glands, causing swelling and discomfort. Understanding how mumps spread and its impact on adults is crucial for prevention and management. Talking to the team of Onlymyhealth, Dr Ravinder Goud Jangampally, Consultant Paediatrician and Neonatologist, Yashoda Hospitals, Hyderabad talked about the transmission of mumps and its implications for different age groups.
Table of Content:-
How Does Mumps Spread?
Dr Jangampally said, “Mumps is an infectious viral illness caused by a type of paramyxovirus that falls under the rubulavirus family. Its primary effect is the painful swelling of the salivary glands. The virus spreads through respiratory droplets and close contact with an infected individual.”
This means that when someone with mumps coughs, sneezes, or talks, tiny droplets containing the virus can spread to others nearby. Additionally, touching surfaces or objects contaminated with these droplets and then touching the mouth, nose, or eyes can also lead to infection.

According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, other organs, such as the pancreas, ovaries, and testes, can also be affected in some cases.
Is Mumps Different for Adults?
Dr Jangampally said that symptoms of mumps appear between 12-25 days after being exposed to the paramyxovirus. According to Johns Hopkins Medicine, while mumps can affect individuals of all ages, its impact can vary depending on the age group. Here's how mumps differs for adults:
Symptoms
Adults may experience more severe symptoms compared to children. Common symptoms include fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, loss of appetite, and swelling of the salivary glands. In some cases, adults may also develop complications such as orchitis (testicular inflammation), oophoritis (ovarian inflammation), meningitis, and encephalitis.
Transmission
Adults can transmit the virus similarly to children, through respiratory droplets. However, adults may have a higher viral load and shed the virus for a longer duration, increasing the risk of spreading mumps to others.
Complications
Adults are more likely to experience complications from mumps, particularly related to reproductive organs. For example, orchitis can lead to testicular swelling, pain, and in rare cases, infertility. Oophoritis, although less common, can cause ovarian inflammation and potential fertility issues in women.
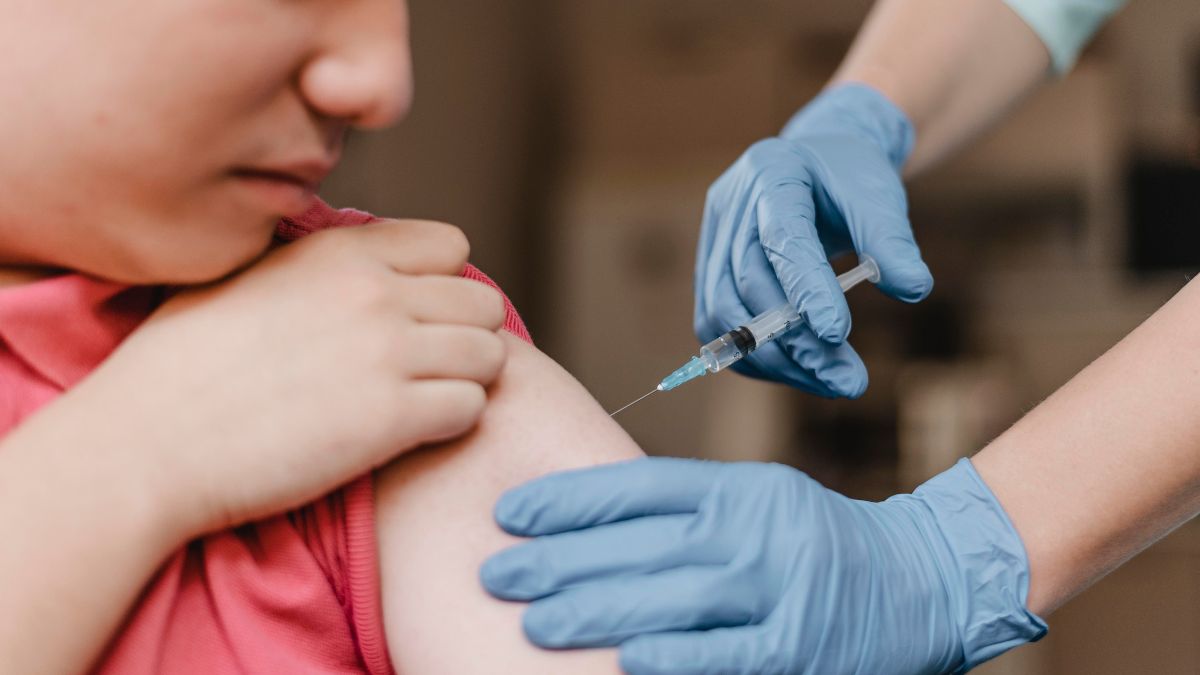
Vaccination Status
Adults who have not been vaccinated or have not received the recommended booster doses are at a higher risk of contracting mumps. Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent mumps and its complications.
Mumps Prevention and Management
“Timely identification and isolation of affected individuals play a crucial role in halting the virus's spread. Individuals who suspect they might have contracted mumps or have had close contact with a confirmed case should promptly consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance,” said Dr Jangampally.
To prevent mumps and reduce its spread, he listed a few steps:
- Vaccination: Ensure you and your family members are up-to-date with the MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine. Vaccination not only protects against mumps but also contributes to herd immunity, reducing the overall prevalence of the virus.
- Hygiene Practices: Practice good respiratory hygiene by covering your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
- Isolation: If you or someone in your household is diagnosed with mumps, follow healthcare guidelines for isolation to prevent spreading the virus to others.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you suspect you have mumps or experience symptoms such as fever and swelling of the salivary glands, consult a healthcare professional for evaluation, diagnosis, and appropriate management.
Also Read: Mumps Could Cause An Epidemic In 2024, Claims IAP: Here Are Its Risk Factors, Preventive Measures
Dr Jangampally concluded that mumps, a viral infection, can lead to considerable discomfort and complications without proper treatment. Recognising its origins, identifying its signs, and adopting preventive measures like vaccination and hygiene practices are crucial in containing its transmission and safeguarding public well-being, whether it is for adults or kids.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version