Every year, Hepatitis Testing Day serves as a reminder for individuals to get tested, raise awareness, and better understand liver health. In 2025, the emphasis remains on early diagnosis and prevention of liver-related conditions, particularly Hepatitis B—a disease often misunderstood and mistaken for jaundice. While both conditions affect the liver, they differ significantly in cause, presentation, and treatment. Here’s a closer look at the fundamental differences between the two.
Table of Content:-
Also Read: Covid Cases In India
Understanding the Liver’s Vital Role
Before exploring the two conditions, it’s crucial to grasp the liver’s essential functions. The liver is the body’s largest internal organ, performing tasks such as:
- Producing bile, which aids in digestion and absorption of fats.
- Filtering toxins from the blood, including alcohol and medications.
- Metabolising drugs, determining how much of a medicine reaches your bloodstream.
- Processing nutrients, converting them into substances your body can use or store.

What Is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver. It’s caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and can be either acute or chronic. Many individuals infected with HBV may not show symptoms, but they can still spread the virus. When symptoms do occur, they may include, yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), fatigue, nausea or vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal discomfort, and dark urine.
Also Read: Gaza’s Grim Toll: 57 Children Dead from Malnutrition Amid Aid Blockade, Says WHO
Hepatitis B spreads through contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. This includes transmission from mother to child during birth, unprotected sex, sharing needles, or using contaminated medical equipment.
In many people, the immune system fights off the virus within a few months. However, if the infection becomes chronic, persisting for more than six months, it can lead to severe liver damage, including cirrhosis or liver cancer.
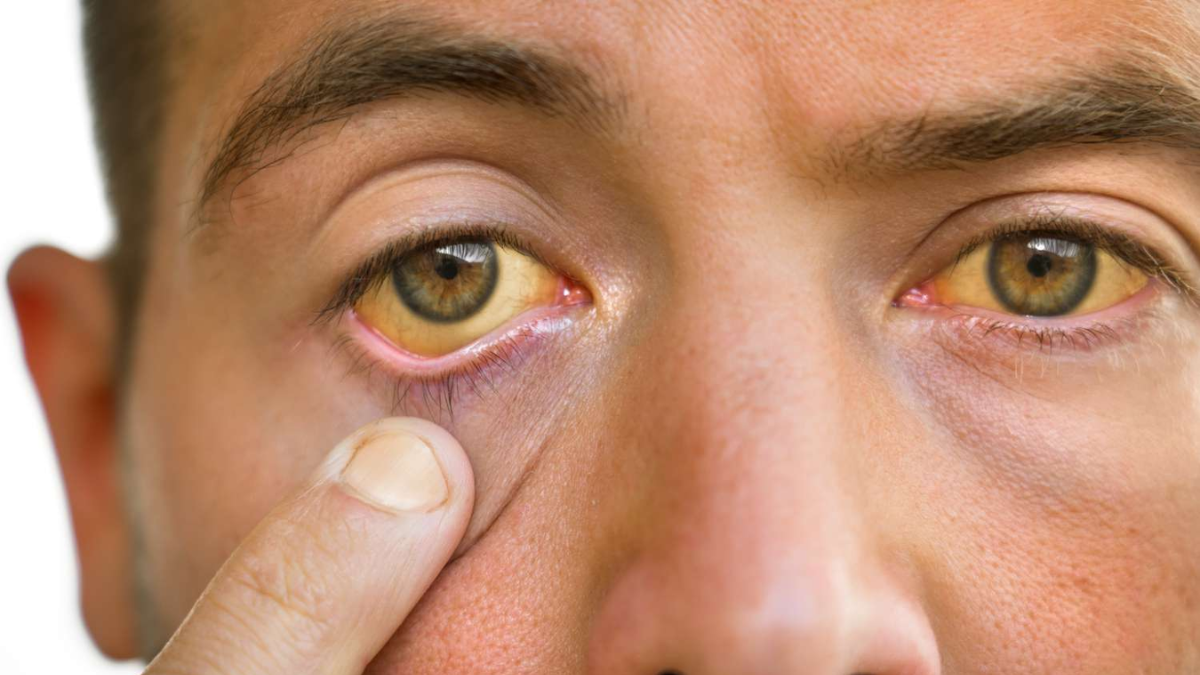
What Is Jaundice?
Unlike Hepatitis B, jaundice is not a disease but a symptom that indicates an underlying problem, often related to the liver or bile ducts. Jaundice results from a buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment that forms when red blood cells are broken down.
Normally, the liver processes bilirubin and helps excrete it via urine or stool. When this process is disrupted, bilirubin accumulates in the blood, leading to yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark-colored urine, pale stools, and itching.
Also Read: 4 Outbreaks In 2025 That Could Signal The Arrival Of Disease X
Jaundice can result from various conditions, such as, liver infections (like Hepatitis A, B, or C), alcohol-related liver damage, hemolytic anaemia, gallstones or tumours blocking the bile duct, and side effects from medications like steroids or certain antibiotics.
Key Differences Between Hepatitis B and Jaundice
Nature of Condition
- Hepatitis B is a viral infection that causes inflammation of the liver.
- Jaundice is a symptom, not a disease—it indicates an underlying issue affecting liver function.
Cause
- Hepatitis B is caused by the Hepatitis B virus (HBV).
- Jaundice results from a buildup of bilirubin, often due to liver or bile duct dysfunction.
Contagiousness
- Hepatitis B is contagious and spreads through contact with infected blood or bodily fluids.
- Jaundice itself is not infectious, though the underlying cause might be (e.g., viral hepatitis).

Symptoms
- Hepatitis B can cause fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, joint pain, and jaundice.
- Jaundice typically presents as yellowing of the skin and eyes, dark urine, pale stools, and itching.
Progression and Risk
- Hepatitis B can become chronic, potentially leading to cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer if untreated.
- Jaundice usually resolves once the underlying cause is treated, but it can signal serious conditions.
Treatment Approach
- Hepatitis B often requires antiviral medications, long-term monitoring, and lifestyle changes.
- Jaundice treatment focuses on addressing the root cause, such as infections, blockages, or medication side effects.

Need for Medical Attention
- Both conditions require medical evaluation, but Hepatitis B particularly needs ongoing care if chronic.
- Jaundice should prompt immediate investigation to uncover its origin.
Importance of Early Testing and Diagnosis
One of the biggest challenges with Hepatitis B is that it can go unnoticed for years. Regular screening is essential, especially for high-risk groups like healthcare workers, intravenous drug users, and people with multiple sexual partners. Testing helps detect the infection early and reduces the risk of complications.
Also Read: Covid 19 Cases Singapore
On the other hand, if jaundice appears, it serves as a warning sign that something is wrong with the liver or biliary system. It should never be ignored, and medical evaluation is necessary to determine its root cause.
Bottomline
This Hepatitis Testing Day 2025, take the opportunity to check in on your liver health. Understanding the difference between Hepatitis B and jaundice can help individuals take the right steps toward prevention, early detection, and treatment. While jaundice may seem like a standalone issue, it often signals deeper problems, sometimes even Hepatitis B itself. Through awareness, testing, and medical guidance, it’s possible to protect one of the body’s most vital organs and ensure long-term health.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version