Gallbladder cancer (GBC) has emerged as a significant health concern, particularly in India, where it contributes to 10% of the global burden. Understanding this malignancy becomes paramount for early detection and effective treatment. Dr. Salil Patkar, Medical Oncologist, Fortis Hiranandani Hospital, Vashi, emphasizes the role of awareness in addressing delayed diagnoses and improving prognoses. Let's delve into seven essential facts about gallbladder cancer, unravelling insights into symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis, stages, survival rates, and preventive measures.
Table of Content:-
Gallbladder Cancer: Facts You Must Know Of
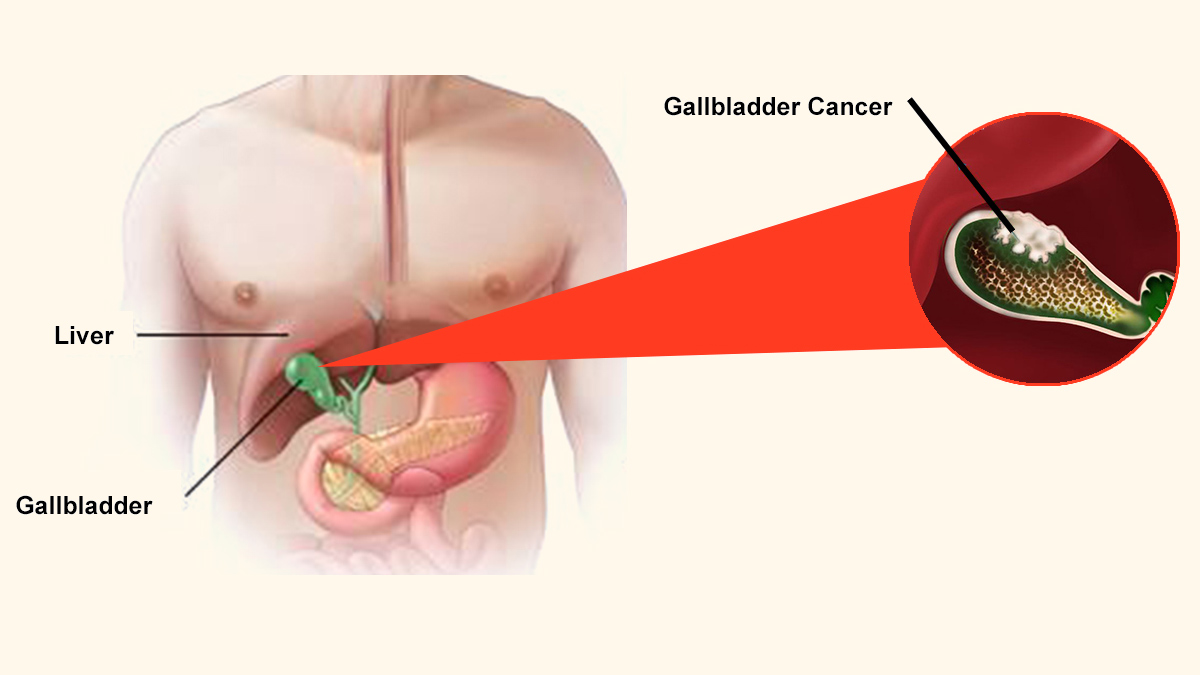
Signs and Symptoms
Early stages of gallbladder cancer may lurk without apparent symptoms, making recognition challenging. However, as the disease progresses, individuals may experience upper-right abdominal pain, unintended weight loss, abdominal bloating, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). Recognizing these signs becomes pivotal for early consultation and timely intervention.
Causes of Gallbladder Cancer
Understanding the root causes of gallbladder cancer is multifaceted:
Also Read: Gallbladder Problems: Things You Need To Know
- Gallstones and Inflammation: A high prevalence of gallstones, chronic inflammation, or infection in the gallbladder serves as a significant risk factor.
- Genetic Factors: A familial predisposition to gallbladder cancer, coupled with genetic conditions, can elevate susceptibility.
- Dietary Influence: Dietary factors, particularly a diet high in fat and low in fibre, prevalent in certain regions of India, contribute to the risk.
- Demographic Factors: Gallbladder cancer is more common in older individuals, with an increased risk associated with age. Furthermore, women are more prone to the disease than men. Geographical variations also play a role, with North India reporting higher rates compared to other regions.
Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the risk of developing gallbladder cancer:
- Gallstones: The presence of gallstones, especially if they cause irritation or infection, stands out as a prominent risk factor.
- Age and Gender: Women are diagnosed with gallbladder cancer more frequently than males, and the disease is more prevalent in individuals over 65 years of age.
Also Read: Gallbladder Removal: Is It Safe And Who Requires It?
Diagnosis of GBC
Diagnosing gallbladder cancer poses challenges, given the symptoms overlap with other digestive disorders. Frequently, diagnostic imaging examinations such as MRIs, CT scans, and ultrasounds are employed. In many instances, early-stage gallbladder malignancies are incidentally discovered during the removal of gallstones.
Stages of GBC
Understanding the progression of gallbladder cancer involves categorizing it into four stages (T1 to T4), based on the extent of cancerous spread:
- T1 and T2: Cancer confined to the gallbladder, representing early stages.
- T3: Localized progression where cancer extends to adjacent organs.
- T4: Metastatic spread, indicating migration to other parts of the body.
The Survival Rate
The 5-year survival rate for gallbladder cancer varies depending on the stage at which it is identified and treated:
- Contained within the gallbladder (T1 and T2): The 5-year survival rate is 62%.
- Spread to nearby tissues or lymph nodes (T3): The rate drops to 27%.
- Metastasized to other areas of the body (T4): The 5-year survival rate plummets to just 2%.
Preventive Measures
While complete prevention may be challenging, adopting a healthy lifestyle, controlling weight, and addressing illnesses that elevate the risk of gallstone formation can significantly reduce susceptibility. Early detection through heightened public awareness remains a key strategy.
Treatment
- Surgical Intervention: Early-stage gallbladder cancer is commonly treated with surgical removal.
- Chemotherapy: Following surgery, patients may undergo chemotherapy to prevent both local and distant recurrence.
- Advanced Stages (III or IV): Treatment involves a combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy, with targeted therapy in certain cases.
Bottomline
Dr Patkar also highlights the importance of public awareness when dealing with health issues such as gallbladder cancer. Public awareness plays a huge role in facilitating early detection, leading to improved outcomes for those impacted by this uncommon but impactful disease.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version