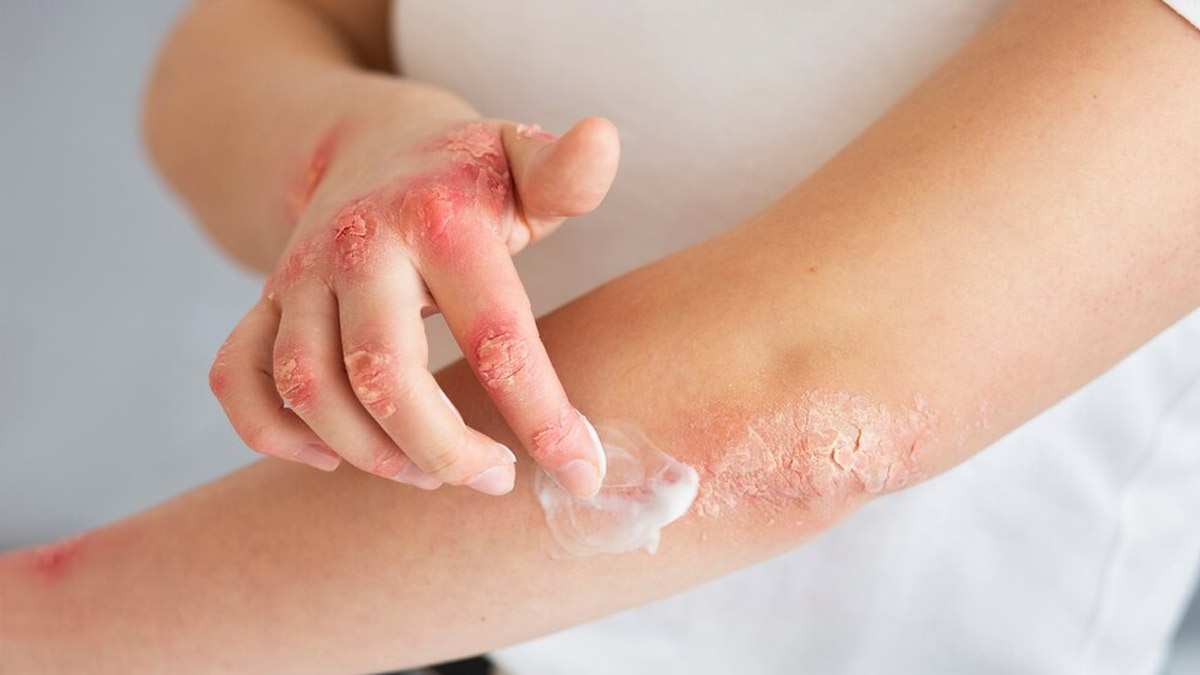
Do you have a persistent skin rash that just won't go away, no matter what you try? Sometimes, a rash can be a sign of an underlying health condition that requires medical attention. Here are some diseases that may be causing your skin rash and what you can do about it.
Table of Content:-
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
The National Eczema Association defines eczema as a common skin condition characterised by red, itchy rashes. It often appears in patches on the face, hands, feet, or behind the knees. Eczema can be triggered by various factors such as allergens, stress, or dry skin. Treatment may include moisturisers, topical corticosteroids, and identifying and avoiding triggers.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to multiply rapidly, leading to thick, scaly patches on the skin, as defined National Psoriasis Foundation. These patches can be itchy and painful. Psoriasis can affect any part of the body, including the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back. Treatment options include topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications prescribed by a dermatologist.
Also Read: Best Ayurvedic Treatment For Skin Rashes And Itching
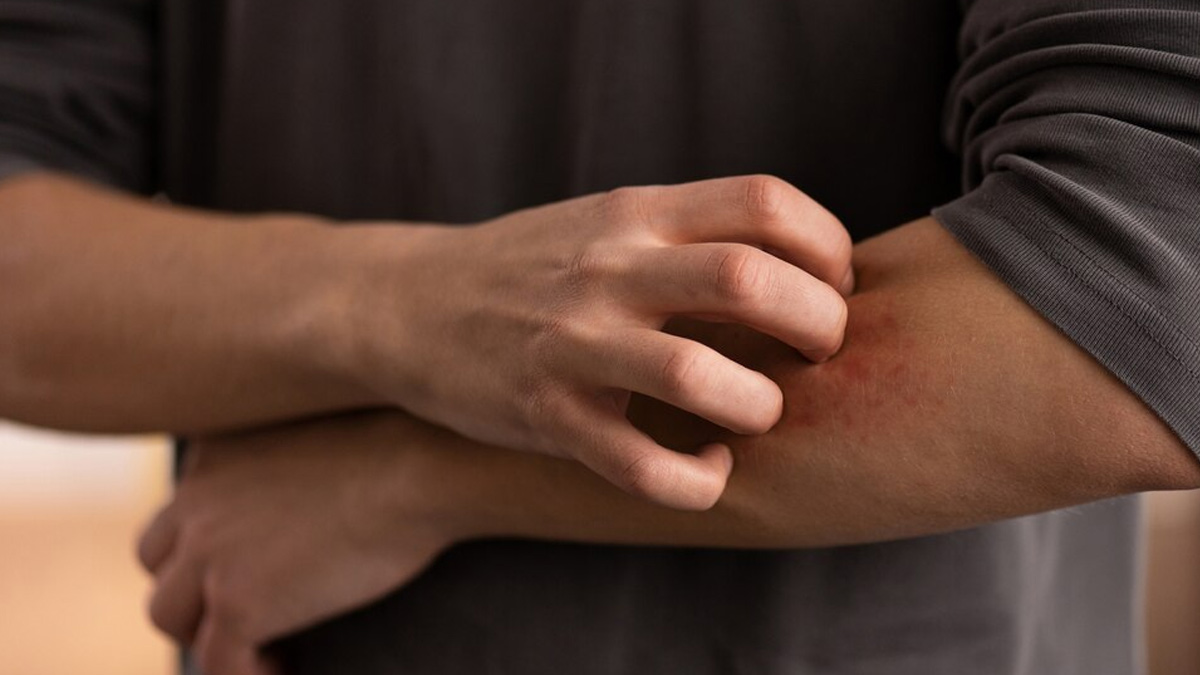

Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen, causing a red, itchy rash. An overview shared that common triggers include soaps, cosmetics, jewellery, and certain plants like poison ivy. Avoiding the trigger and using soothing lotions or corticosteroid creams can help alleviate symptoms.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections such as ringworm, candidiasis, and tinea versicolor can cause skin rashes. These infections thrive in warm, moist environments and are often characterised by redness, scaling, and itching. Antifungal medications, both topical and oral, are used to treat fungal infections.
Lupus
The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defined lupus as an autoimmune disease that can affect the skin, joints, organs, and other systems in the body. One common skin manifestation of lupus is a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, but it can also cause other types of rashes, sensitivity to sunlight, and skin lesions. Managing lupus requires a comprehensive treatment plan coordinated by a rheumatologist.
Also Read: From Itchy Skin Rashes To Swelling In The Mouth, Warning Signs Of Wheat Allergy
Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and acne-like bumps. The National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases shared that triggers for rosacea include sun exposure, spicy foods, alcohol, and stress. Dermatological treatments like topical creams, oral medications, and laser therapy can help manage rosacea symptoms.
Scabies
Scabies is a contagious skin infestation caused by microscopic mites, according to the CDC. It leads to intense itching and a red, bumpy rash, often in the folds of the skin and between fingers and toes. Treatment involves topical scabicidal creams and thorough cleaning of clothing and bedding to prevent re-infestation.
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH)
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, DH is a skin manifestation of celiac disease, characterised by itchy, blistering rashes, typically on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and scalp. A gluten-free diet is the primary treatment for DH, along with medications to control symptoms.
If you're experiencing a persistent skin rash that isn't improving or causing discomfort, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Ignoring skin rashes or attempting self-diagnosis can lead to worsening symptoms and complications. Remember to take care of your skin and seek medical advice when needed for optimal skin health.
Also watch this video
Read Next
Billie Eilish Once Opened Up About Her Tourette's Syndrome; Know All About Diagnosis And Treatment
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version