Hepatitis is now the second leading infectious cause of death worldwide. According to the latest report by the World Health Organisation (WHO), the number of deaths attributed to viral hepatitis is on the rise. This statistic, with 1.3 million deaths annually, places it on par with tuberculosis, another major infectious disease.
The 2024 Global Hepatitis Report by WHO underscores a concerning trend where despite advancements in diagnostic tools, treatment options, and reduced product costs, there has been a stagnation in testing and treatment coverage rates. The data reveals a significant increase in estimated deaths due to viral hepatitis, rising from 1.1 million in 2019 to 1.3 million in 2022. Among these fatalities, 83% were attributed to hepatitis B, while 17% were linked to hepatitis C. Shockingly, approximately 3500 individuals succumb to hepatitis B and C infections every day globally.
Although both Hepatitis B and C are primarily spread through bodily fluids, there are definite distinctions between the two forms of viral hepatitis, each with unique characteristics, modes of transmission, and preventive measures.
Hepatitis B Vs Hepatitis C
The data indicates that 254 million individuals are living with hepatitis B and 50 million with hepatitis C as of 2022. Half of these chronic infections burden people aged 30–54 years, with 12% affecting children under 18. Males constitute 58% of all hepatitis cases.
However, despite the concerning incidence, global diagnosis and treatment rates for chronic hepatitis B and C are inadequate. Only 13% of those with chronic hepatitis B were diagnosed, and a mere 3% received antiviral therapy by the end of 2022. Similarly, 36% were diagnosed with hepatitis C, and only 20% received curative treatment.
What is Hepatitis B?
As per WHO, Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It is transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. HBV can be acute, meaning it lasts for a short time and resolves on its own, or chronic, where the infection persists for more than six months and can lead to serious liver complications.
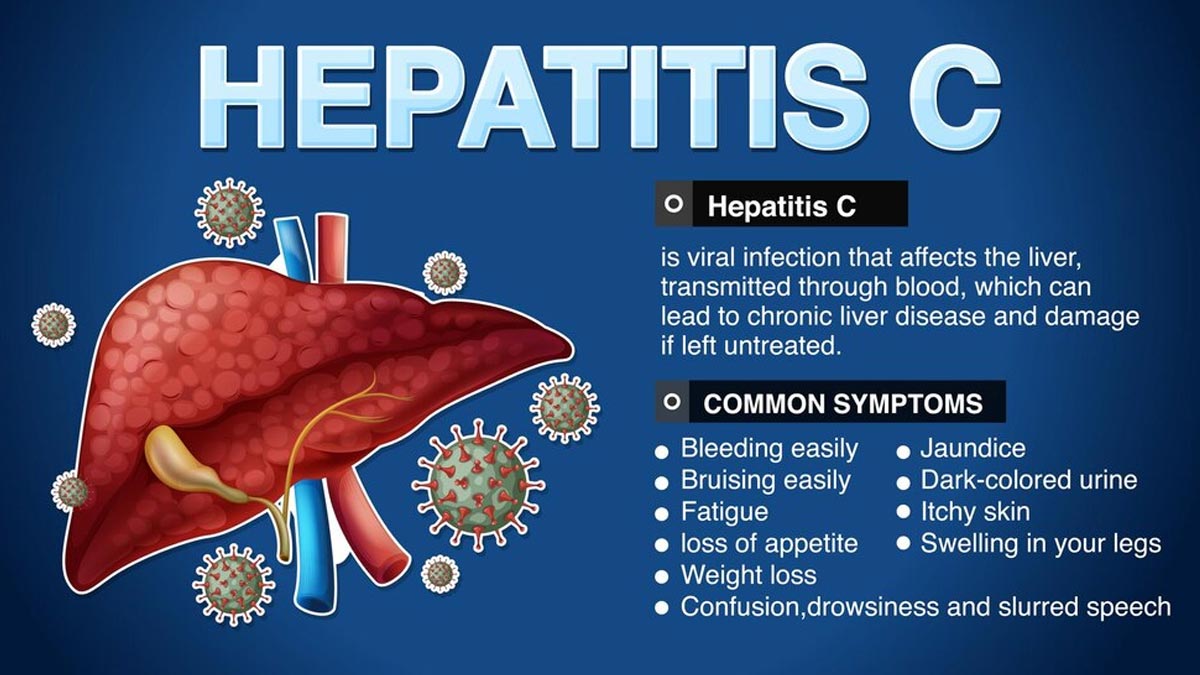
What is Hepatitis C?
Hepatitis C is also a viral infection of the liver, caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV), said the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention. It is transmitted primarily through exposure to infected blood, often through sharing needles or other drug-injecting equipment. HCV can also be transmitted through sexual contact, though this is less common.
Key Differences Between Hepatitis B and C
Hepatitis B and C are very close in nature. Here’s how you can differentiate between the two/
Mode of Transmission
HBV: Transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen, or other bodily fluids. Can also be transmitted from mother to baby during childbirth.
HCV: Primarily transmitted through exposure to infected blood, such as sharing needles or receiving blood transfusions from infected donors.
Also Read: 5 Risk Factors Of Hepatitis That Should Urge You To Take A Test
Chronicity
HBV: This can result in chronic infection in some cases, especially when acquired at birth. Chronic HBV infection can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
HCV: More likely to cause chronic infection than acute infection. Chronic HCV infection can also lead to liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and other complications.
Vaccine Availability
HBV: There is an effective vaccine available to prevent Hepatitis B infection. The vaccine is recommended for all infants and unvaccinated adults at risk of exposure.
HCV: There is currently no vaccine available for Hepatitis C. Prevention relies on avoiding behaviours that can lead to exposure, such as sharing needles or having unprotected sex with infected individuals.
Treatment Options
HBV: Antiviral medications are available to treat chronic Hepatitis B and reduce the risk of complications. Regular monitoring and medical care are essential for managing the infection.
HCV: Antiviral medications are also available to treat chronic Hepatitis C. Advances in treatment have led to highly effective therapies with high cure rates for most individuals.
Preventive Measures for Hepatitis B and C
One area where you don’t need to make much distinctions between the two strains of Hepatitis is ways to prevent both:
- Vaccination: Get vaccinated against Hepatitis B to prevent infection. Vaccination is particularly important for infants, healthcare workers, and individuals at risk of exposure.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use condoms during sexual activity, especially with new or multiple partners, to reduce the risk of Hepatitis B and C transmission.
- Avoid Sharing Needles: Do not share needles or syringes for drug use, tattoos, or piercings. Use sterile equipment and avoid risky behaviours that can lead to blood exposure.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands regularly, especially after using the bathroom and before handling food, to prevent the spread of Hepatitis B and C.
- Seek Medical Care: If you suspect you have been exposed to Hepatitis B or C, or if you experience symptoms such as fatigue, jaundice, or abdominal pain, seek medical attention promptly for testing and treatment.
Also Read: Viral hepatitis: Lifestyle Measures You Should Follow To Prevent It

Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General, expressed concern, stating, "This report highlights a troubling scenario: despite global progress in preventing hepatitis infections, fatalities are escalating due to inadequate diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis patients." However, achieving the WHO's elimination target for hepatitis by 2030 remains feasible if immediate and decisive actions are taken. By understanding the key differences between Hepatitis B and C, and following preventive measures such as vaccination, safe sex practices, and avoiding risky behaviours, we can do our part to reduce the risk of infection. Stay informed, stay safe!