
Emilia Clarke, widely recognised for her role as Daenerys Targaryen on HBO’s "Game of Thrones," has recently shed light on her harrowing experiences with two brain aneurysms. These medical emergencies occurred during the peak of her career, adding immense pressure and anxiety to an already demanding role. Clarke, now 37, revealed in an interview with Big Issue how these incidents profoundly affected her sense of self and her professional life.
Table of Content:-
The Impact on Her Career and Personal Life
During the candid interview, Clarke discussed how the aneurysms and subsequent brain surgeries significantly altered her perception of herself and her abilities. “When you have a brain injury, because it alters your sense of self on such a dramatic level, all of the insecurities you have going into the workplace quadruple overnight,” she explained. The fear of not being able to perform her job due to potential cognitive impairments was overwhelming. Clarke recalled the anxiety she felt, fearing she might be deemed incapable of fulfilling her role: “The first fear we all had was: ‘Oh my God, am I going to get fired? Am I going to get fired because they think I’m not capable of completing the job?’”
The stress was compounded by the intense nature of her work. Portraying a character as iconic as Daenerys Targaryen is no small feat, and the pressure to deliver a flawless performance was immense. Clarke mentioned a particularly dark thought that crossed her mind: “Well if I’m going to die, I better die on live TV,” highlighting the extreme stress she endured while dealing with her medical condition.
View this post on Instagram
Understanding Aneurysms
As per Dr Nishant Shanker Yagnick, Senior Consultant - Neurology, Manipal Hospitals, Gurugram, an aneurysm is a localised, blood-filled balloon-like bulge in the wall of a blood vessel, often an artery. The primary arteries in the body carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the rest of the body. When part of an artery wall weakens, it can lead to an aneurysm. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause severe complications, including death.
Symptoms of an Aneurysm
Aneurysms can often go unnoticed until they rupture. Some common symptoms that might indicate the presence of an aneurysm, depending on its location, include:
- Severe headaches
- Lightheadedness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Pain in the head, chest, abdomen, or back
- Sudden loss of consciousness
- Vision changes
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue
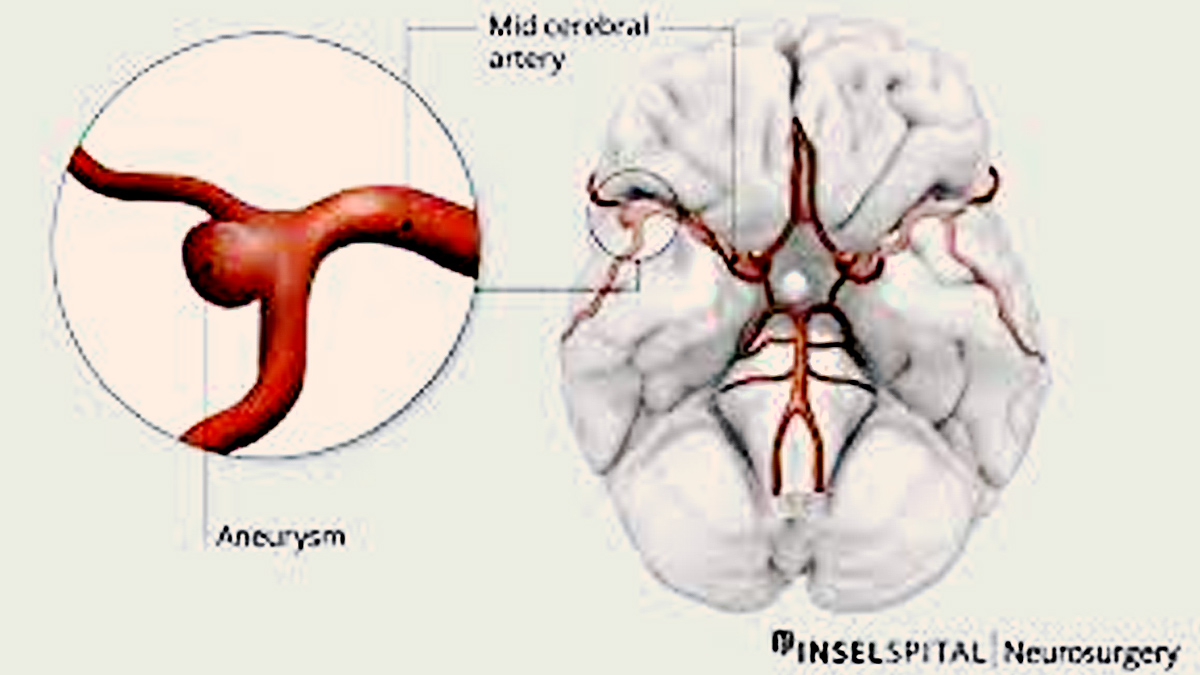
Complications Arising from Aneurysms
If an aneurysm ruptures, it leads to internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening. A brain aneurysm rupture, known as a subarachnoid haemorrhage, causes what is often described as the worst headache of one’s life, accompanied by other severe symptoms like limb weakness and speech difficulties. Ruptured aneurysms can lead to strokes, further exacerbating the risk of long-term damage or fatality.
Causes of Aneurysms
Aneurysms can be congenital or develop over time due to various factors. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries)
- High blood pressure
- Family history of aneurysms
- Trauma or injury to blood vessels
Also Read: Post Malone Weight Loss: How Shedding 55 lbs Turned His Career And Life Around
Treatment Options for Aneurysms
Treatment for aneurysms depends on their size, location, and risk of rupture. For unruptured aneurysms, close monitoring and lifestyle changes may be sufficient. However, if there is a high risk of rupture, medical intervention is necessary. Treatment options include:
Medication
Medications can help manage conditions that contribute to aneurysm growth, such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, thus reducing the pressure on artery walls.
Surgical Procedures
- Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR): A minimally invasive surgery where a catheter is used to insert a graft that reinforces the weakened artery.
- Open Surgery: Involves a direct approach to either reinforce or remove the aneurysm through an incision.
- Endovascular Coiling: Primarily used for brain aneurysms, where coils are inserted into the aneurysm to disrupt blood flow and prevent rupture.
- Microvascular Clipping: A type of open brain surgery where a clip is placed at the base of the aneurysm to cut off its blood supply.
- Catheter Embolization: A catheter is used to introduce substances that block the blood flow to the aneurysm.
Bottomline
Emilia Clarke’s journey through her health struggles and her determination to continue her career despite the odds is truly inspirational. Her openness about her experiences brings much-needed awareness to the realities of living with and recovering from aneurysms. Clarke's story underscores the importance of medical awareness and the resilience of the human spirit in the face of life-threatening challenges.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version