Lung cancer has long been associated with smoking, but an alarming issue has emerged in India that non-smokers are being diagnosed with lung cancer at an earlier age compared to their Western counterparts. This shift highlights the need for increased awareness, early detection, and proactive measures to combat this deadly disease in India.
Table of Content:-
Lung cancer in non-smokers is becoming more prevalent in India. A recent study by Lancet shows that non-smoking Indians are being diagnosed with lung cancer in their 40s and 50s, significantly earlier than non-smokers in Western countries, who are typically diagnosed in their 60s and 70s. This disturbing problem is raising concerns among healthcare professionals and researchers alike.
To understand this in detail, OnlyMyHealth interacted with Dr Arun Chowdary Kotaru, Consultant, Respiratory and Sleep Medicine at Artemis Hospital Gurugram.
Possible Causes
Several factors could be contributing to this trend in India:
Air Pollution
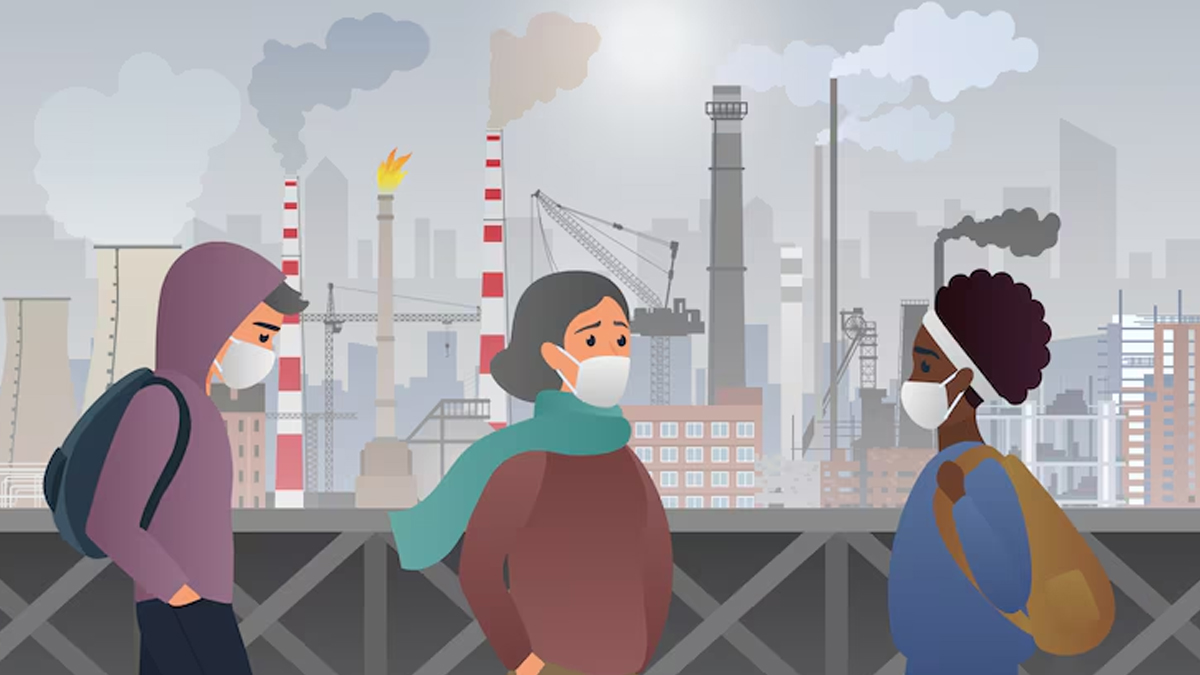

India’s urban areas are notorious for their high levels of air pollution. Dr Kotaru said, “Long-term exposure to pollutants such as PM2.5 and PM10, found in vehicle emissions, industrial waste, and construction dust, can damage lung tissue and increase cancer risk.” Studies have shown a direct correlation between air pollution and lung cancer, particularly among non-smokers.
Indoor Pollution
Many Indian households use biomass fuels like wood, cow dung, and crop residues for cooking and heating. The smoke generated from these fuels contains harmful carcinogens, which, when inhaled over time, can lead to lung cancer.
Genetic Factors
According to Dr Kotaru, genetic predisposition plays a significant role in cancer susceptibility. “Certain genetic mutations, more prevalent in the Indian population, may make individuals more vulnerable to lung cancer,” Dr Kotaru said. Research into these genetic links is ongoing, but initial findings suggest a higher risk among Indians.
Also read: Can Shoulder Pain Be A Sign Of Lung Cancer?
Passive Smoking
Exposure to secondhand smoke is another critical factor. In densely populated areas, non-smokers may be involuntarily exposed to cigarette smoke in public places, workplaces, and even at home. Dr Kotaru said that this passive smoking can have similar harmful effects as active smoking.
The Importance of Early Detection

Early detection is crucial in improving lung cancer outcomes. Sharing concerns, Dr Kotaru said, “Unfortunately, lung cancer in non-smokers often goes undiagnosed until it reaches an advanced stage due to the lack of awareness and screening programs.” Symptoms like persistent cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath are often attributed to less severe conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
In India, there is a pressing need to implement widespread screening programs, especially for high-risk individuals, regardless of their smoking status. Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scans have proven effective in detecting early-stage lung cancer and should be made accessible and affordable to the broader population.
Also read: Lung Cancer: Vital Role Of Scans For The Smokers Over 50
Raising Awareness and Advocacy
Public awareness campaigns are vital in educating people about the risks of lung cancer, particularly for non-smokers. Highlighting the role of air pollution, indoor smoke, and passive smoking in lung cancer development can encourage individuals to take preventive measures.
Advocacy for cleaner air policies is also crucial. Stricter regulations on emissions, promoting the use of cleaner fuels, and improving indoor ventilation can significantly reduce exposure to harmful pollutants.
Conclusion
The rising incidence of lung cancer among non-smoking Indians at an earlier age than Westerners is a cause for concern. It underscores the urgent need for increased awareness, early detection, and preventive measures. By addressing the contributing factors such as air and indoor pollution, genetic predispositions, and passive smoking, India can make strides in reducing the burden of lung cancer.
Also watch this video
How we keep this article up to date:
We work with experts and keep a close eye on the latest in health and wellness. Whenever there is a new research or helpful information, we update our articles with accurate and useful advice.
Current Version